Acquisition processing
The acquisition process is two-fold:
- straightforward retrieval and reformatting of altimeter data
- synchronization process in order to freeze altimetry flow processing until reception of all ancillary data needed for complete processing.
The DUACS system takes as input L2 altimeter products. The measurements ([O/I]GDR or equivalent) from different altimeters are retrieved.
In NRT processing, the acquisition step uses two different data flows: the OGDR/NRT flow (within a few hours), and the IGDR/STC flow (within a few days). The acquisition software detects, downloads and processes incoming data as soon as they are available on remote sites (external database, FTP site). Data are split into passes if necessary. This processing step delivers “raw” data that have been divided into cycles and passes, and ordered chronologically.
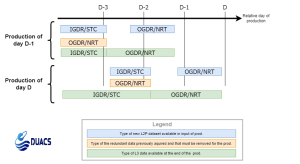
For each OGDR/NRT input, the system checks that no equivalent IGDR/STC entry is available in the data base before acquisition; for each IGDR/STC input, the system checks and deletes the equivalent OGDR/NRT entry in the data base. These operations aim to avoid duplicates in the DUACS system. This processing is summarized in figure 1.
In addition to L2 altimeter products, the DUACS system also acquires auxiliary data needed to calculate geophysical corrections such as atmospheric pressure at sea level, wind stress, polar tide, etc. (see “Homogenization and cross-calibration section” for details). This acquisition is done only when the required standards are not available on upstream L2 products. The acquisition of the auxiliary data is synchronized with the acquisition of L2 altimeter products.
Figure 1 : Overview of the near real time system data flow management
In the NRT system, full-rate (typically 20Hz) altimeter measurements are acquired when available, Otherwise, low-rate (1Hz) measurements are considered. The following table lists the sampling-rate used for the different altimeters.
Table : Sampling-rate of the different altimeters used in the NRT L3 production.
| Altimeter mission | NTC(IGDR)/NRT(OGDR) Sampling-rate used (Hz) |
| Sentinel-6A | 20 |
| Sentinel-3A/B | 20 |
| Jason-3 | 20 |
| Cryosat-2 | 1 |
| SARAL-DP/AltiKa | 1 |
| SWOT-nadir | 20 |
| HaiYang-2B | 20 |
In DT system, the GDR/NTC data flow, with the 1Hz posting rate, is used. The acquisition is activated specifically before each DT production.
The number of altimeters processed varies with time as summarized in Figure 2 and Figure 3.

Figure 2: Evolution of the number of altimeters processed in NRT conditions. See Copernicus Marine product section for details.
Figure 3: Evolution of the number of altimeters processed for the MY DT-2024 series. See Copernicus Marine product section for details.
Input data quality control
The L2 Input Data Quality Control is a critical process applied to guarantee that DUACS uses only the most accurate altimeter data. The quality control is based on various indicators. It relies on (i) standard raw data editing with quality flags or parameter thresholds for altimeter, radiometer and geophysical corrections; (ii) complex data editing algorithms based on the detection of erroneous artifacts affecting the consistency of each pass; (iii) mono and multi-mission crossover validation; and (iv) macroscopic statistics to edit out large data flows that do not meet the system’s requirements. Details of threshold editing can be found in the handbook of each altimeter mission (e.g., Aviso+, 2020, 2022).
Thanks to the high quality of current missions, this process rejects only a small percentage of altimeter measurements, but this small amount of erroneous data could be the cause of a significant quality loss.